|
|
|
|
The spread of monkeypox has many people concerned, which is understandable given how another viral disease – COVID-19 – upended the globe after early reports of apparent community spread. Microbiologist Rodney Rohde from Texas State University, who works in the area of diseases with animal origins, provides a picture of this smallpox cousin, with some reassuring context on transmission.
As anyone living in the western part of the U.S. knows all too well, a drought has persisted since 2020. But even parts of the U.S. that are projected to see a net increase in annual precipitation are not immune to droughts, writes University of Colorado Boulder research scientist Imtiaz Rangwala, who describes the effects of our “hotter, thirstier atmosphere.” “As humanity enters a hotter future, prolonged periods of weeks to months of below-normal precipitation
are going to be of a greater concern almost everywhere,” he writes.
If you’ve ever been curious about intermittent fasting to lose weight, nutritional scientist McKale Montgomery from Oklahoma State University gives you a scientific explanation, starting with how body metabolism works. She also reviews the literature that shows the effectiveness of fasting for reducing weight and disease risk, even while noting that results from standard calorie-restricted diets are not significantly different.
Also in this week’s science news:
If there’s a subject you’d like our team of science editors to investigate, please reply to this email.
|

|
Martin La Monica
Director of Editorial Projects and Newsletters
|
|
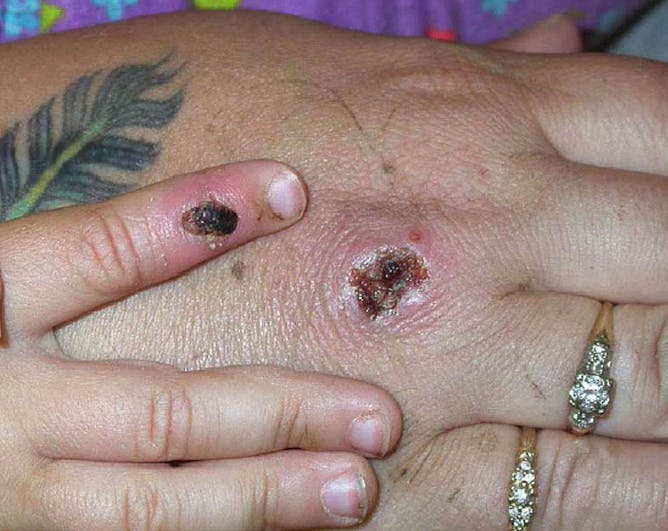
Monkeypox causes lesions that resemble pus-filled blisters, which eventually scab over.
CDC/Getty Images
Rodney E. Rohde, Texas State University
Monkeypox has been spreading in humans since as early as 1970. While most monkeypox infections are mild, some can be fatal.
|
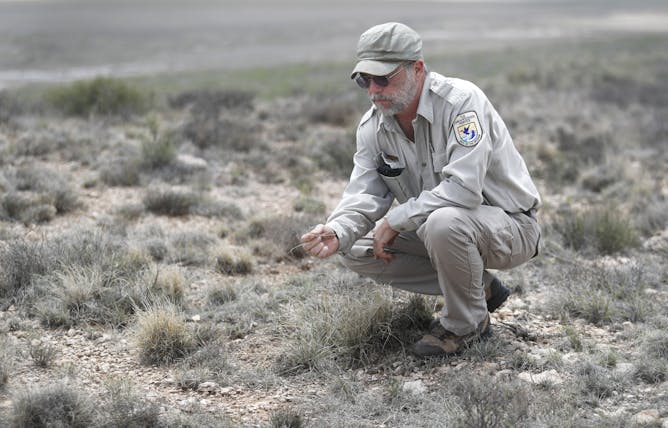

Farmers in some regions are being encouraged to preserve and establish grasslands that can survive drought and protect the soil.
AP Photo/Mark Rogers
Imtiaz Rangwala, University of Colorado Boulder
La Niña is only part of the problem. The long-term driver of increasing drought – even in areas getting more rainfall overall – is the rapidly warming climate.
|
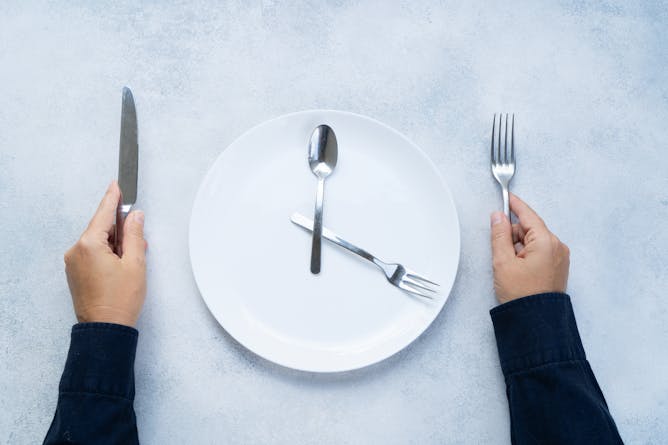

Intermittent fasting could have an array of health benefits, but as of yet there are no long-term studies into its effects.
neirfy/iStock via Getty Images Plus
McKale Montgomery, Oklahoma State University
Proponents of intermittent fasting say the clock can help you win the battle of the bulge. But the science behind it is a little more complicated.
|
|
|
-
Sourav Sengupta, University at Buffalo
Psychotherapy is not one size fits all. From behavioral to gestalt therapies, which approach will work best for you depends on your needs and goals.
-
Daniel Macfarlane, Western Michigan University
Cleaning up the Great Lakes was a big job when the US and Canada undertook it in 1972. Today it’s far more challenging.
-
Kellen Chen, University of Arizona
Skin grafts for severe burn injuries may require multiple operations over the course of a lifetime to address crippling scars.
-
Daniella McCahey, Texas Tech University
Scientists just grew plants in soil from the Moon, but Antarctica has long provided researchers with the perfect place to test their agricultural techniques for a future in space.
-
Artemis Spyrou, Michigan State University; Dennis Mücher, University of Guelph
Nuclear isomers are rare versions of elements with properties that mystified physicists when first discovered. Isomers are now used in medicine and astronomy, and researchers are set to discover thousands more of them.
-
Christina Polomoff, University of Connecticut
Studying medication use in a traumatized population of immigrants required pharmacists to listen to and learn from trusted community health workers.
-
James Edward Huchingson, Florida International University
A professor of religion and science explains different views on immortality, from the religious perspective of President Jimmy Carter to the scientific, secular take of Carl Sagan.
-
C. Michael White, University of Connecticut
Prescription opiods, stimulants such as those used to treat ADHD and the ingredients found in sexual dysfunction drugs like Viagra are some of the drugs that are being marketed to US consumers.
|
|
|
| | |
| | |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
|