|
|
|
|
My backyard this spring and summer has seen a conspicuous bump in wildlife: a brood of scurrying squirrels, raucous blue jays, chipmunks, fledged robins, tiny rabbits and the like. It’s around this time of year that people are likely to bump into a young animal that may look like it’s lost or needs help.
Should you intervene? To answer that question, we contacted Penn State wildlife biologist Julian Avery, who says that people’s efforts to help animals often end up doing more harm than good, although there are exceptions, such as helping a turtle or other slow-moving creature to cross a road. “When I do intervene, it is after carefully considering the potential reasons for the animal’s situation, the species’ population status and the potential harm my actions
might inflict upon the whole population – not just on one adorable creature,” he writes.
It seems as if every week there’s more evidence of the importance of eating whole foods, such as unprocessed fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, nuts and seeds, as opposed to ultraprocessed products. As University of Washington gastroenterologist Christopher Damman notes, a food’s fiber content signals – via your gut microbiome – how your body should metabolize food. His story explains the science of how our bodies digest carbohydrates and the importance of
fiber, not just for weight but also blood sugar and overall health.
Some of the stories our regular readers enjoyed over the past week include one on how dialects in England were barriers to starting families across group boundaries, a report on the “breathtaking scale and invasive nature of the consumer data market” and how it has enabled government agencies to surveil citizens, and a recounting of scientists in the South Pole detecting the first neutrino emissions from within the Milky Way.
Also in this week’s science news:
If there’s a subject you’d like our team of science editors to investigate, please reply to this email.
|

|
Martin LaMonica
Director of Editorial Projects and Newsletters
|
|
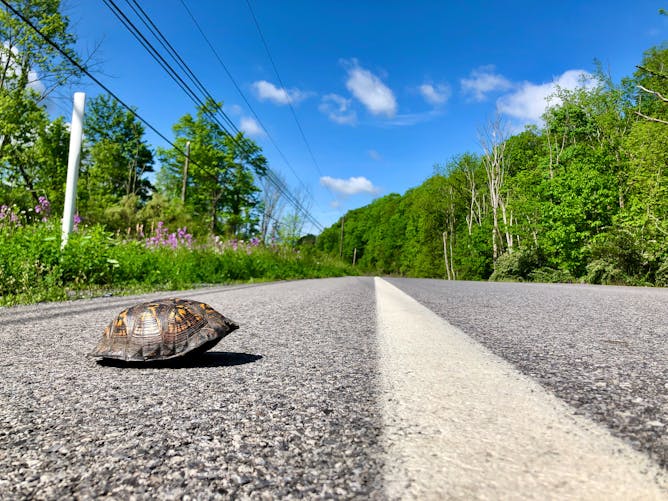

An eastern box turtle crossing a rural Pennsylvania road.
Julian Avery
Julian Avery, Penn State
A newborn bison calf in Yellowstone National Park had to be euthanized after a visitor handled it in May 2023 – a recent example of how trying to help wild animals often harms them.
|
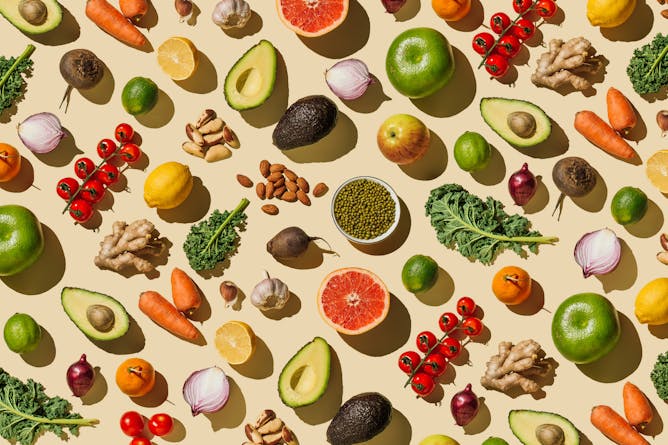

Whole foods like unprocessed fruits, vegetables and grains are typically high in fiber.
Tanja Ivanova/Moment via Getty Images
Christopher Damman, University of Washington
Many processed foods strip carbs of their natural fibers. Eating foods with an ideal total carbohydrate-to-fiber ratio can help with weight management and improve overall health.
|
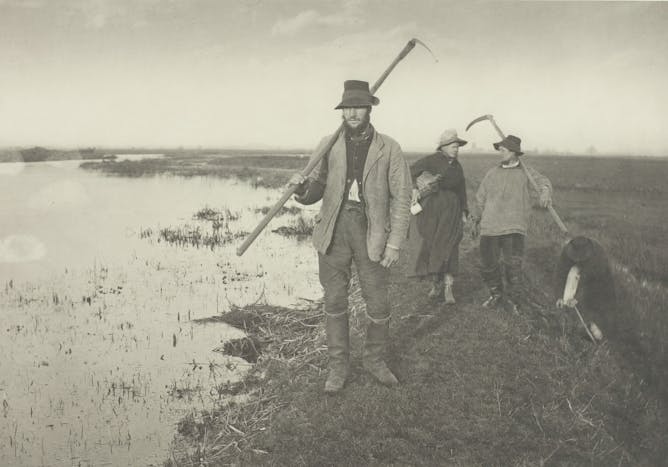

Conditions in rural England around the turn of the 20th century offer a case study for cultural evolution researchers.
Heritage Images/Hulton Archive via Getty Images
Yakov Pichkar, Vanderbilt University; Nicole Creanza, Vanderbilt University
People with a common history – often due to significant geographic or social barriers – often share genetics and language. New research finds that even a dialect can act as a barrier within a group.
|
|
|

Andrew N. Cleland, University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering
Scientists show they can create quantum superpositions of sound particles, pointing to the potential for mechanical quantum computers.
| |

Mojtaba Sadegh, Boise State University
Nearly 22 million people lived within 3 miles of a US wildfire in the past two decades. A new study tracking their locations flips the script on who is at risk.
|
Megan Keller, Cornell University; Tobias Dörr, Cornell University
Researchers uncovered the foundations of biology by using E. coli as a model organism. But over-reliance on this microbe can lead to knowledge blind spots with implications for antibiotic resistance.
| |

Zdenka Myslikova, Tufts University; Nathaniel Dolton-Thornton, Tufts University
China is a major investor in Latin America’s renewable energy and critical minerals like lithium, but countries like Chile are also taking steps to secure their own clean energy future.
|

Sanya Carley, University of Pennsylvania; David Konisky, Indiana University
One in 4 American households are at risk of losing power because of the high cost of energy. Over 30% of those disconnections are in summer, when heat gets dangerous.
| |

Chris Impey, University of Arizona
Astronomers have for the first time detected the background hum of gravitational waves likely caused by merging black holes.
|

Rajiv Chowdhury, Florida International University
After recent cases in Florida and Texas, authorities are advising the public to drain standing water sources to keep mosquitoes from multiplying.
| |

Vahe Peroomian, USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences
With two eclipses and several meteor showers coming up, an astronomy professor shares travel tips for viewing astronomical phenomena.
|
|
|
|
|
-
Jim Madsen, University of Wisconsin-Madison
New data from the IceCube collaboration shows neutrino emissions from within our Milky Way galaxy – but figuring out where exactly these ghost particles come from is harder than it seems.
-
Alun Hubbard, University of Tromsø
Glaciologists are discovering new ways surface meltwater alters the internal structure of ice sheets, and raising an alarm that sea level rise could be much more abrupt than current models forecast.
-
Yunkang Yang, Texas A&M University; Matthew Hindman, George Washington University; Trevor Davis, Columbia University
The flood of misinformation on social media could actually be worse than many researchers have reported. The problem is that many studies analyzed only text, leaving visual misinformation uncounted.
-
Rodney E. Rohde, Texas State University
An aggressive, antifungal-resistant form of tinea, a contagious ringworm fungal infection, has appeared in the US, likely driven by overuse and misuse of antifungal medications.
|
|
|
| | |
| | |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
|