|
The announcement that Moscow and Kyiv had signed an agreement allowing Ukraine to resume grain exports was greeted with great relief in capitals across the world. The anticipation was that the deal would help blunt the growing global food crisis. A blockade of Ukraine’s ports as a result of the war had left an estimated 22mn tonnes of wheat, corn and other grains stranded in silos. But the optimism was short held. A Russian missile attack on the port of Odesa within 24 hours of the deal being signed put a question mark over Moscow’s intentions. Nevertheless, the hope is that the deal will hold, which, as Wandile Sihlobo explains, will have immediate benefits. Grain prices could soften as more supplies become
available to the world market. Overall this would be a good development for consumers, particularly those living in poor developing nations.
The deadly Marburg virus has claimed the lives of two people in Ghana. Marburg is a hemorrhagic fever virus, like Ebola, and is high infectious. Nigerian professor of virology Oyewale Tomori unpacks Marburg’s symptoms, how it spreads and the precautions necessary for protection against it. Preventing the spread of infection is the most potent weapon given that there is no treatment. He advocates early detection through improved surveillance and early
diagnosis.
|

Wandile Sihlobo, Stellenbosch University
If Russia keeps its word, the benefits will be immediate. Grain prices could soften as more grain supplies become available to the world market.
|
Oyewale Tomori, Nigerian Academy of Science
The chances of surviving Marburg are improved if there’s early supportive care with rehydration and symptomatic treatment.
|
|
|
-
Patricia Hynes, Sheffield Hallam University
Sir Mo Farah took three decades to discuss what happened to him as a child.
-
Thomas Stewart, Penn State
The newly discovered species – Qikiqtania – highlights evolution’s twisty, tangled path.
-
Lotte Hughes, The Open University
Just over 100 years ago, Maasai in Kenya were moved into reserves, where they could be more easily taxed and controlled, to make way for white settlement.
-
William Petri, University of Virginia
The oral polio vaccine – which is no longer given in the US – relies on a live but weakened virus that can actually be passed from person to person.
-
Christine Keiner, Rochester Institute of Technology
Zebra and quagga mussels entered the Great Lakes in large ships’ ballast water. Now, local boaters and anglers are spreading them into the southern and western US.
|
|
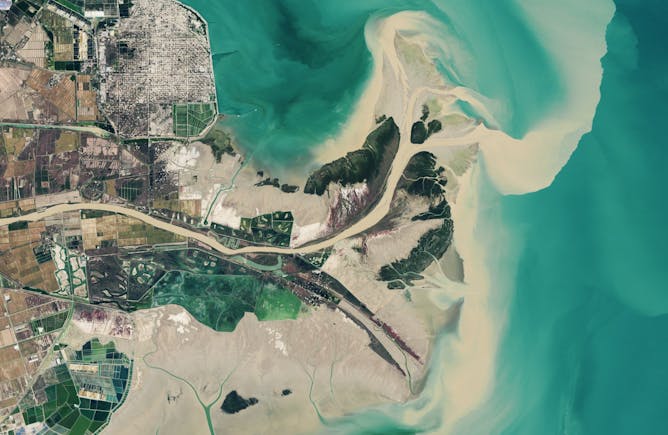

Stacy Morford, The Conversation
With decades of images and data from the same locations, these satellites can show changes over time, including deforestation, changes in waterways and how loss of trees corresponds to urban heat.
|