|
This year’s Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine went to Svante Pääbo, a pioneer in the field of ancient DNA who reconstructed the genomes of our extinct fellow hominids, Neanderthals and Denisovans. His groundbreaking work gave researchers powerful new tools to take on a host of new questions and introduced complex questions around the use of ancient skeletons, writes Rice University anthropologist Mary Prendergast. She sketches out where this fast-evolving field is heading and some of the challenges ahead.
The Supreme Court heard oral arguments on Monday in a case that could lead to narrowing federal protections on wetlands. In this story, Penn State ecologist Jon Sweetman explains what a wetland is from a scientific perspective, and how these critical habitat areas are at threat from development and farming. “Since 1970, the planet has lost 35% of its wetlands, a rate three times faster than the loss of forests,” he writes.
A 10-year-old from Bengaluru, India, wrote in with a question about déjà vu that led to this revealing story by Colorado State University cognitive psychologist Anne Cleary, who has studied the phenomenon. Her team used virtual reality to test the idea that similar scenes can trigger déjà vu – imagine a person having an eerie feeling of having been in that place before when walking up to a hospital reception that was similar to one they had seen before. “Very likely, many factors can contribute to what makes a scene or a situation feel familiar,” she writes.
Also in this week’s science news:
|

Researchers need to be careful not to contaminate ancient samples with their own DNA.
Caia Image via Getty Images
Mary Prendergast, Rice University
Thousands of ancient genomes have been sequenced to date. A Nobel Prize highlights tremendous opportunities for aDNA, as well as challenges related to rapid growth, equity and misinformation.
|

A raccoon with a fish at the Corkscrew Swamp Sanctuary in Naples, Fla.
Michael Siluk/UCG/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
Jon Sweetman, Penn State
The US Supreme Court opens its 2022-2023 term with a case that could greatly reduce federal protection for wetlands. Here is what makes these ecosystems valuable.
|

How can someplace you’ve never been feel so familiar?
mrs/Moment via Getty Images
Anne Cleary, Colorado State University
While people have wondered about déjà vu for a long time, only recently have scientists started experimentally investigating what might trigger it.
|
|
|
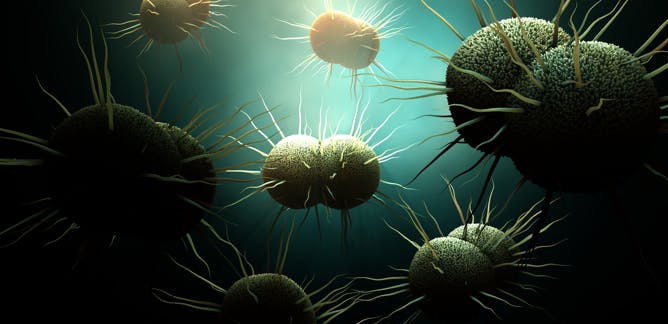
Kenneth Keiler, Penn State
The US currently has only one antibiotic available to treat gonorrhea – and it’s becoming less effective.
| |

Rachel A. Davis, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
This rare procedure is offered by only a handful of centers in the US and around the world and should be used only when less invasive treatment options for OCD have been tried.
|

Mathew Barlow, UMass Lowell; Suzana J. Camargo, Columbia University
Two hurricane and climate scientists explain what’s known – and still unknown – about global warming’s influence on intensity, rainfall and much more.
| |

Brad Spellberg, University of Southern California; Jaimo Ahn, University of Michigan; Robert Centor, University of Alabama at Birmingham
How doctors care for their patients is highly influenced by clinical guidelines. Recommendations based on anecdotal experience or poor data can harm patients.
|
|
|
|
|
-
Mark Lorch, University of Hull
The three scientists’ independent discoveries are helping to make the entire field of chemistry more environmentally friendly.
-
Thomas Schrepfer, University of Florida; Rex Haberman, University of Florida
Perhaps surprisingly, it’s possible to get swimmer’s ear without a dip in the pool, lake or ocean. Two doctors explain what this painful infection is and how to get rid of it.
-
Rodney E. Rohde, Texas State University
On World Rabies Day – which is also the anniversary of French microbiologist Louis Pasteur’s death – a virologist reflects on the achievements of this visionary scientist.
-
Andrea Marpillero-Colomina, The New School
Reducing air pollution from cars and light trucks would pay big health dividends for low-income and minority communities. A new survey shows how to get more drivers of color into electric vehicles.
-
Robert Young, Lancaster University
The discovery that particles can be spookily connected has lead to a technological revolution.
|
|