|
|
|
|
In a research review U.K. researchers last year challenged the long-held belief that people with depression suffer from a chemical imbalance in the brain, kicking off a broader debate about treatment for depression.
University of Michigan’s Elissa H. Patterson and Jay Kayser note the clinical status quo, with its heavy emphasis on medication, is not very effective. Nearly three out of four people who take antidepressants do not get complete relief from their symptoms, which can lead to people’s conditions being categorized as “treatment-resistant depression.” They detail many alternatives to medications, some of which may sound familiar but, they contend, have not been integrated into the profession. “The things we do on a day-to-day basis, called lifestyle factors, function as building blocks for a life without depression,” they write.
People who live in the Northeast U.S, as I do, know what a mild winter we’ve had. The lab of Boston University biologist Richard Primack has been researching how climate change affects annual rhythms such as the arrival of leaves and migration of birds in the springtime, using the extensive records of Henry David Thoreau in Concord, Massachusetts, for many studies. In his latest article for us, Primack and his colleagues looked more broadly and found that “as temperatures warm, deciduous trees across eastern North America are advancing their leaf-out timing faster than native wildflowers are responding.” This mismatch can mean that in some regions native
wildflowers are more likely to be shaded out by trees.
One of the most well-read science stories last week was a study on the advanced communication abilities of bees, which teach younger bees with a “waggle dance” where to forage. Our editors also uncovered a study on widely inconsistent EPA enforcement of pollution laws by state, and an ethicist makes the case that the biggest risk from generative AI such as ChatGPT is people’s tendency to attach human characteristics to our tools and machines.
Also in this week science news:
If there’s a subject you’d like our team of science editors to investigate, please reply to this email.
|

|
Martin La Monica
Director of Editorial Projects and Newsletters
|
|

A diagnosis of treatment-resistant depression can lead to a sense of hopelessness and despair in some patients.
Maria Korneeva/Moment via Getty Images
Elissa H. Patterson, University of Michigan; Jay Kayser, University of Michigan
An overreliance on medication as the first-line treatment for depression can lead some people to be labeled with treatment-resistant depression when there are other viable alternatives for relief.
|
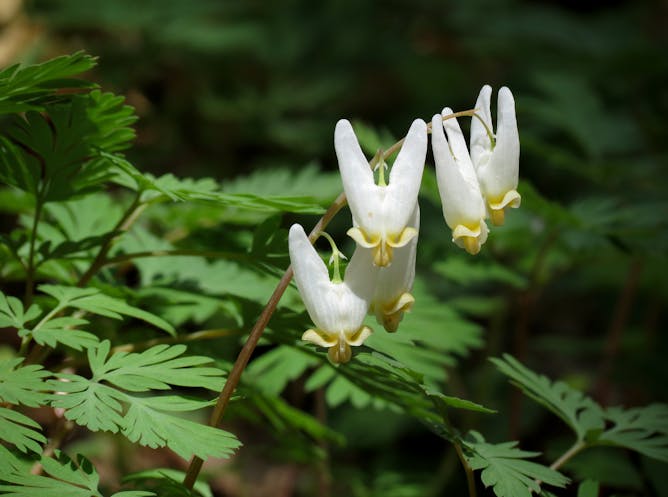

Native wildflowers, such as these Dutchman’s breeches (Dicentra cucullaria) that bloom early in spring are losing access to sunlight as trees leaf out earlier.
Katja Schulz/Flickr
Richard B. Primack, Boston University; Benjamin R. Lee, University of Pittsburgh; Tara K. Miller, Boston University
Many beloved wildflowers bloom in early spring, while trees are still bare and the flowers have access to sunlight. Climate change is throwing trees and wildflowers out of sync.
|
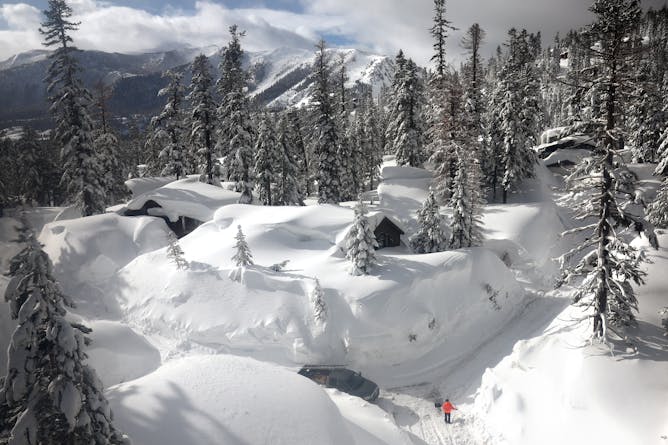

A series of atmospheric rivers in early 2023 covered the Sierra Nevada in snow.
Mario Tama/Getty Images
Keith Musselman, University of Colorado Boulder
Another atmospheric river is hitting the state, raising flood risks as rain falls on deep snowpack. Rain on snow is also a growing problem as the planet warms.
|
|
|

Laurence Zwiebel, Vanderbilt University; Stephen Ferguson, Vanderbilt University
Researchers explore what happens when ants can’t properly use smell to detect friend from foe.
| |

Aditi Gurkar, University of Pittsburgh
Aging is a major risk factor for many chronic diseases. Figuring out what influences longevity and how to identify rapid agers could lead to healthier and longer lives for more people.
|

Manil Suri, University of Maryland, Baltimore County
Pi gets a lot of attention this time of year, but there are plenty of other mathematical constants just as deserving of recognition.
| |
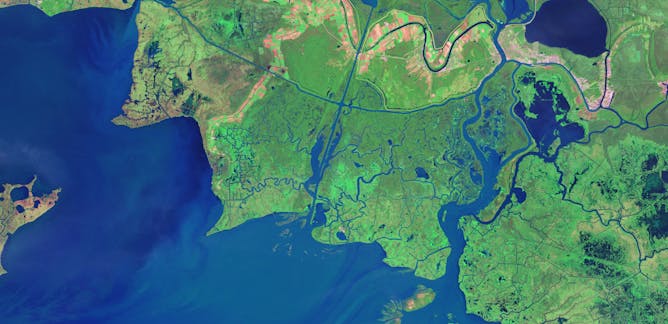
Qiusheng Wu, University of Tennessee
Time-lapse animations that once took days to create are now easy to build with publicly available satellite images and free online tools.
|

Nir Eisikovits, UMass Boston
Our tendency to view machines as people and become attached to them points to real risks of psychological entanglement with AI technology.
| |

Fred Martin, UMass Lowell
Almost everybody uses the internet just about every day. But do you really know what the internet is?
|

Eva Fisher, Colorado State University Global; Fugen Neziroglu, Hofstra University; Jamie Feusner, University of Toronto
About a quarter of those with body dysmorphic disorder attempt suicide or struggle with ideas of suicide. Fortunately, medication and therapy have proved highly effective at treating the disorder.
| |

James C. Nieh, University of California, San Diego
Honeybees possess one of the most complex examples of nonhuman communication. New research suggests that it is learned and culturally passed down from older to younger bees.
|
|
|
|
|
-
Frank Han, University of Illinois at Chicago; Jennifer H. Huang, Oregon Health & Science University
Parsing the risk of myocarditis from viral infection versus vaccination is challenging, and researchers are intensely studying the various factors that are at play.
-
Susan Lawrence, University of Tennessee; Susan E. Lederer, University of Wisconsin-Madison
This particularly physical kind of philanthropy caught on in the mid-20th century.
-
Beverly Law, Oregon State University; William Moomaw, Tufts University
Protecting old and mature trees is the simplest and least expensive way to pull carbon out of the atmosphere – but proposed logging projects threaten mature stands across the US.
-
Jerry Anderson, Drake University
A new study reveals wide disparities among state-issued Clean Water Act fines, and even among federal fines from regions to region. A law professor explains why it may be illegal.
-
Adam Hume, Boston University; Elke Mühlberger, Boston University; Judith Olejnik, Boston University
The Marburg virus, a close cousin of Ebola, currently has no approved treatments or vaccines to protect against it.
|
|
|
| | |
| | |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
|